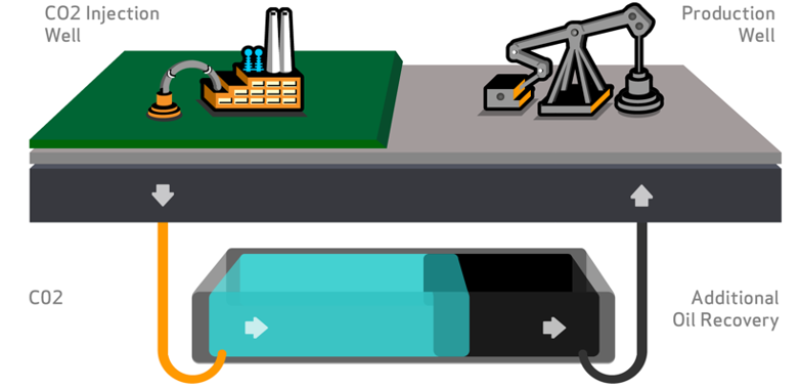
The complete paper is based upon a company’s experience with regard to carbon dioxide (CO2) enhanced oil recovery (EOR) studies on asset integrity, material selection, and corrosion mitigation. The paper discusses the main factors affecting CO2 corrosion, provides an assessment of what to look for in major equipment, and details recommended material of construction and corrosion mitigation/control methods.
CO2 Corrosion
Along with the benefits of injection of CO2 comes the risk of internal corrosion. Dry CO2 gas is not itself corrosive, but is so when dissolved in an aqueous phase (water is required for corrosion to occur). CO2 is extremely soluble in water and brine and has even greater solubility in hydrocarbons. CO2 dissolves into the crude oil and follows the production and transportation process, and it can dissolve in water and react with iron in carbon steel pipes.