Reservoir simulation
The index integrates three independent components extracted from static and dynamic parameters: reservoir permeability thickness, movable gas, and reservoir pressure from a historically matched dynamic model.
This paper develops a deep-learning work flow that can predict the changes in carbon dioxide mineralization over time and space in saline aquifers, offering a more-efficient approach compared with traditional physics-based simulations.
The authors of this paper propose a hybrid approach that combines physics with data-driven approaches for efficient and accurate forecasting of the performance of unconventional wells under codevelopment.
-
This paper describes a full-field and near-wellbore poromechanics coupling scheme used to model productivity-index degradation against time.
-
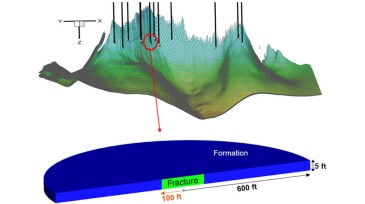
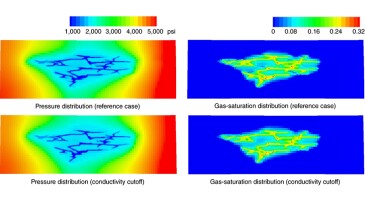
The authors of this paper present an advanced dual-porosity, dual-permeability (A-DPDK) work flow that leverages benefits of discrete fracture and DPDK modeling approaches.
-
This study presents a novel approach to screen thermally stable surfactants at high pressures and high temperatures for the explicit purpose of wettability alteration in the operator’s Eagle Ford acreage.
-
The authors of this paper write that computationally coupled models enable swift, accurate, and engineered decision-making for optimal asset development.
-
The authors of this paper describe a model-driven work flow developed for hydraulic fracturing design and execution that could be a resource for other shale plays with similar challenges worldwide.
-
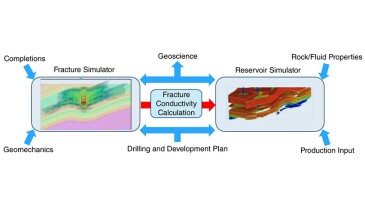
This paper presents a case study of integrated geomechanical and reservoir simulation with a developed fracture conductivity calculation work flow to evaluate well spacing and completions design.
-
The authors of this paper describe a procedure that enables fast reconstruction of the entire production data set with multiple missing sections in different variables.
-
This paper presents a physics-assisted deep-learning model to facilitate transfer learning in unconventional reservoirs by integrating the complementary strengths of physics-based and data-driven predictive models.
-
This article presents the application of a reinforcement learning control framework based on the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient. The crack propagation process is simulated in Abaqus, which is integrated with a reinforcement learning environment to control crack propagation in brittle material. The real-world deployment of the proposed control framework is also dis…
-
A new program offers an affordable way to figure out if salt precipitation could be behind underperforming gas wells and suggests a path to higher production.
Page 1 of 14